Learn how blockchain technology in supply chain is revolutionizing industry standards. Explore the benefits, impacts, and advancements that blockchain brings to supply chain management.
Contents
Basic of Blockchain Technology
Definition of Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology represents a groundbreaking approach to digital record-keeping, designed to offer a secure and transparent method of recording transactions. It is fundamentally a decentralized digital ledger where data is stored across a network of computers.
Each record, or “block,” contains a set of verified transactions linked in chronological order, creating a chain. This structure ensures that once a block is added to the chain, it is virtually immutable, providing a reliable and unalterable history of transactions.

Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases managed by a single entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. Each participant has a copy of the blockchain, and transactions are verified collectively, eliminating single points of control and failure. This decentralization enhances resilience and reduces the risk of data manipulation.
Security: Blockchain technology utilizes cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure chain. The consensus mechanism, required to add new blocks, ensures that data cannot be altered without agreement from the majority of the network. This robust security framework makes blockchain resistant to tampering and fraud.
Transparency: All transactions recorded on a blockchain are visible to participants in the network, ensuring a high level of transparency. This visibility allows for real-time tracking and verification of transactions, fostering trust among participants.
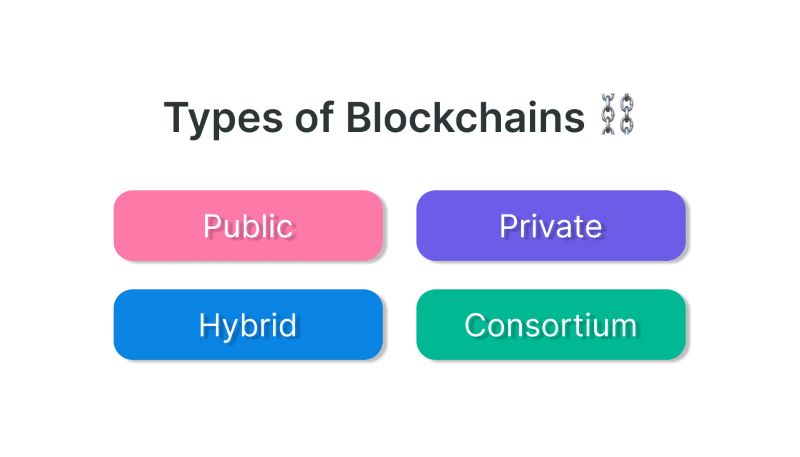
Types of Blockchains
Public Blockchains: These are open networks where anyone can join and participate. Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are designed for transparency and decentralization, with no need for permission to access or participate in the network. They are ideal for applications where openness and inclusivity are critical.
Private Blockchains: In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains are restricted and accessible only to authorized participants. These are often used within organizations or closed networks where control and privacy are essential. Private blockchains offer enhanced confidentiality and efficiency for internal processes.
Consortium Blockchains: Consortium blockchains are semi-private and involve multiple organizations or entities. They require permission from a predefined group of participants to join. This type of blockchain is useful for collaborative efforts among multiple parties, offering a balance between privacy and shared control.
Hybrid Blockchains: Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains. They offer a blend of public accessibility and private control.
Blockchain and Supply Chain Integration
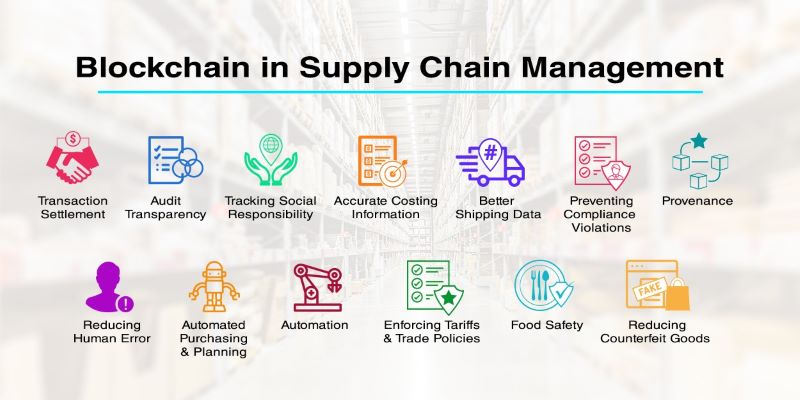
The integration of blockchain technology into supply chain management represents a significant leap forward in enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security. As global supply chains become increasingly complex, blockchain offers a robust solution to address many of the challenges faced by traditional systems.
This integration can revolutionize how products are tracked, verified, and managed throughout their lifecycle.
Benefits of Blockchain technology in Supply Chain Management
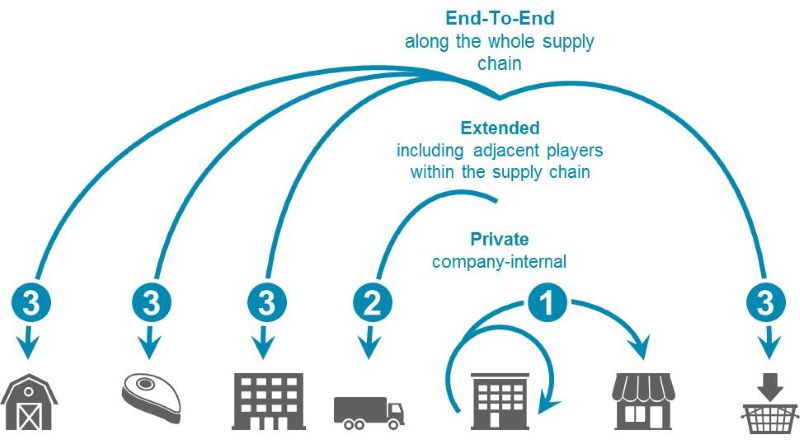
Transparency and Traceability of Goods in Transit
Imagine you are working with unique Lego pieces, only viewable to a select group of people. This analogy captures the essence of how blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain transparency. In business, timely and accurate information is crucial, and blockchain enhances this by providing real-time visibility and verifiability to all authorized parties. As supply chains grow more complex, this transparency significantly reduces the risk of fraud and ensures accountability throughout the network.
When an error occurs, blockchain allows all members to trace activities back to the source of the issue, facilitating quick resolution. For customers, having access to such transparency fosters trust and peace of mind, making blockchain a valuable tool in building strong relationships with logistics partners.
Enhanced Security of Supply Chain
In an era where cybercrime is escalating and supply chains are increasingly intricate, blockchain offers robust security features. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes immutable—meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This permanence creates a transparent and tamper-proof record, making it easier to prevent and detect fraud.
Blockchain’s decentralization further enhances security by distributing data across a network rather than relying on a single central authority. This reduces the risk of cyberattacks and unauthorized access. For example, in e-health, decentralization allows for secure and anonymous storage of patient records on blockchain, enabling data analysis without compromising patient privacy.
Efficiency and Automation of Information in Supply Chain
Blockchain introduces smart contracts, which are self-executing programs that automate and enforce contract terms. Once predefined conditions are met, these contracts trigger actions such as issuing invoices, streamlining processes and eliminating the need for intermediaries. This automation speeds up transactions, enhances compliance, and improves overall efficiency.
In inventory management, blockchain’s transparency allows manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors to collaborate seamlessly. Approved parties can track product flow and verify transactions, ensuring order fulfillment and fostering trust in the legitimacy of invoices. This efficiency benefits businesses by improving cash flow management and reducing administrative overhead.
Challenges of Blockchain technology in supply chain
Scalability
Blockchain networks, especially those using proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, often face scalability issues. As the supply chain expands and more transactions occur, the demands on processing power, storage capacity, and energy consumption increase.
Every transaction is recorded across all nodes, leading to large data storage requirements that can strain the network. Solutions such as sharding or layer-two protocols are being explored to enhance scalability, but companies must carefully plan their blockchain deployment to ensure it meets their specific supply chain needs without compromising efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance
The decentralized nature of blockchain creates challenges in adhering to varying regulatory standards across different countries and regions. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union poses challenges for blockchain’s immutable and transparent ledger, which can conflict with data protection principles.
Organizations must navigate these regulations by employing privacy-enhancing technologies like zero-knowledge proofs or off-chain storage. Collaboration between blockchain developers, supply chain stakeholders, and regulators is essential to establish industry standards and guidelines that ensure compliance with legal requirements, including trade sanctions and product certifications.
Interoperability
As blockchain adoption increases, the lack of interoperability between different blockchain platforms poses a significant challenge. Each blockchain may have its structure, consensus mechanism, and smart contract language, making data exchange and integration across multiple platforms difficult.
The current solutions, such as off-chain relayers and bridges, are often resource-intensive and costly. To address this, industry-wide collaboration is needed to develop common standards and protocols that enable seamless integration and interoperability among different blockchain systems, ensuring end-to-end compatibility across supply chains.
Industry Adoption
Widespread adoption of blockchain in supply chain management is hindered by factors such as the perceived complexity of the technology, integration challenges with existing systems, and a lack of understanding of its benefits. Achieving universal industry adoption requires the alignment and cooperation of all stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and regulatory bodies.
However, this can be challenging due to varying levels of trust and conflicting interests. Industry-wide education and awareness programs are crucial to demonstrate blockchain’s potential, address concerns, and showcase successful use cases to encourage broader adoption.
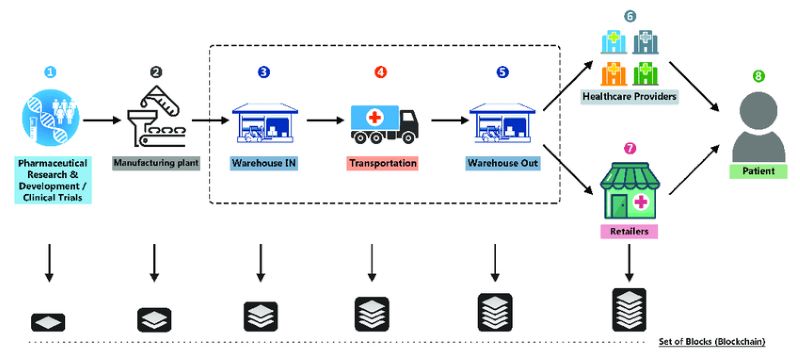
Application of Blockchain technology in Supply Chain Management
Traceability
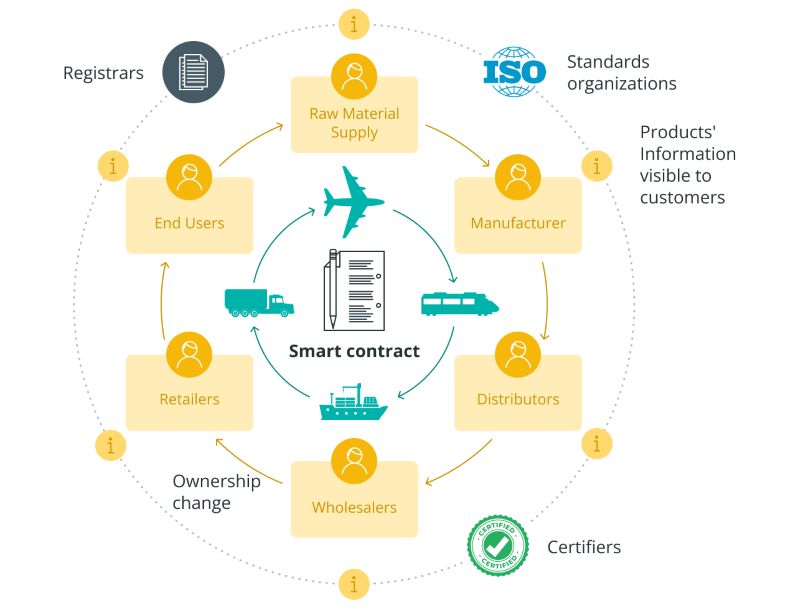
Blockchain’s ability to create an immutable ledger of every product’s journey makes it an invaluable tool for traceability in supply chains. By documenting each step from the origin to the final destination, businesses can ensure the accuracy and integrity of their supply chains.
This high level of traceability not only enhances accountability but also plays a critical role in product recalls and quality assurance, allowing consumers to trust the products they purchase and fostering strong relationships between companies and customers.
Transparency
Traditional supply chains often lack visibility, leading to trust issues among participants. Blockchain addresses this challenge by providing a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger accessible to all stakeholders.
Every transaction is recorded transparently and cannot be altered, establishing a single source of truth for all parties involved. This transparency allows for real-time tracking of goods from raw materials to finished products, helping businesses identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks, ultimately improving supply chain operations.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements encoded on the blockchain with predefined conditions. In supply chain management, these contracts automate various processes like procurement, payments, and compliance, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing errors or disputes.
For example, a smart contract can automatically trigger payment to a supplier when a shipment reaches its destination, enhancing efficiency and ensuring all contractual obligations are met.
Inventory Management
Blockchain’s secure and transparent ledger helps address inefficiencies and inaccuracies in traditional inventory management systems. By integrating IoT devices and sensors, real-time data on inventory levels, locations, and conditions can be recorded on the blockchain.
This transparency helps stakeholders monitor inventory more effectively, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts, and optimizing supply chain operations.
Compliance
Blockchain’s immutable nature makes it ideal for maintaining a reliable and auditable record of all supply chain transactions. This capability helps businesses demonstrate compliance with regulations, standards, and certifications. By securely storing and sharing data, such as certificates of origin and quality inspections, blockchain ensures the authenticity of compliance documents.
Additionally, smart contracts can automate compliance processes, ensuring all participants adhere to regulatory requirements, thereby reducing risks and enhancing trust within the supply chain ecosystem.
Blockchain technology in supply chain is reshaping the way industries operate by boosting transparency, security, and efficiency. As businesses continue to adopt this cutting-edge technology, it’s clear that blockchain is setting new standards and driving significant improvements. For further insights into how blockchain can enhance your supply chain operations, visit Dwelling Tech Trends.
